7 2 X 1 2
thesills
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
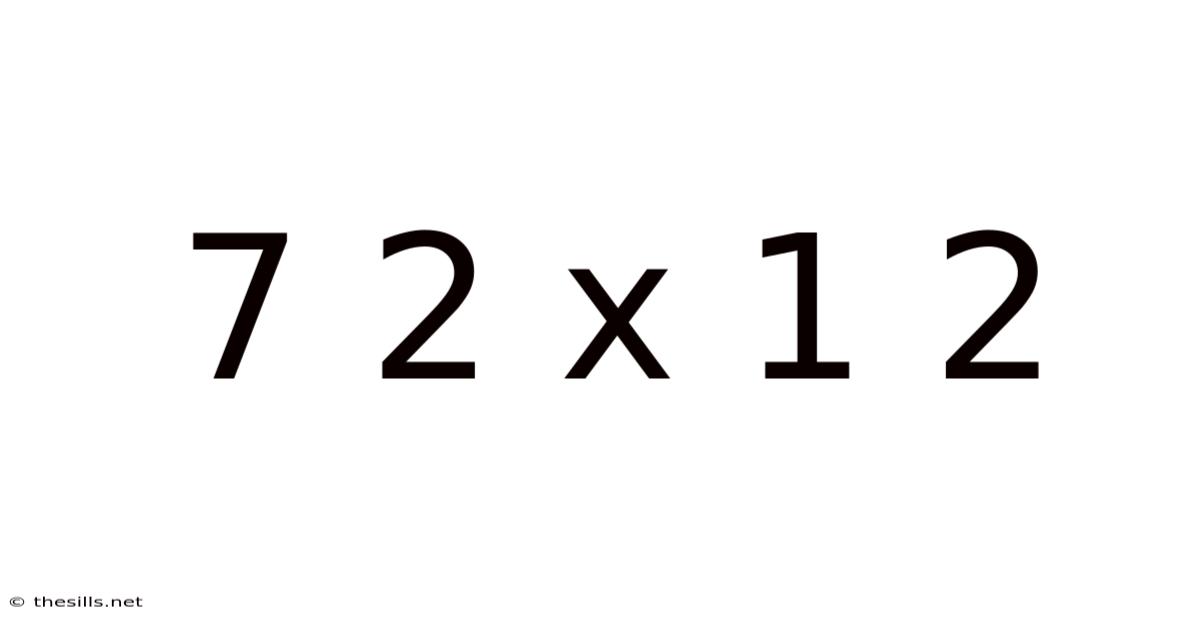
Table of Contents
Decoding 7 x 2 x 12: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical equation, 7 x 2 x 12, delving far beyond the basic calculation to uncover the underlying principles of multiplication, its practical applications in various fields, and its significance in developing a strong mathematical foundation. We'll explore different methods of solving this problem, examine related mathematical concepts, and discuss real-world scenarios where this type of calculation is crucial. Understanding multiplication, even in its simplest form, is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and essential for navigating numerous aspects of daily life and advanced studies.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication as Repeated Addition
At its core, multiplication is simply a shorthand way of performing repeated addition. The equation 7 x 2 x 12 can be interpreted as adding seven twos twelve times, or adding twelve sevens two times, or any combination thereof. This fundamental understanding is crucial, especially when introducing the concept to younger learners. Visual aids, such as arrays (organized sets of objects arranged in rows and columns), can effectively demonstrate this relationship. For example, representing 7 x 2 visually could involve seven rows of two objects each.
Calculating 7 x 2 x 12: Different Approaches
There are several ways to approach solving 7 x 2 x 12, all yielding the same result. The order of operations (often remembered by the acronym PEMDAS/BODMAS) dictates that multiplication can be performed in any order. This flexibility is advantageous, allowing us to choose the method that feels most intuitive or efficient.
-
Method 1: Sequential Multiplication: We can solve this equation sequentially, starting from left to right. First, 7 x 2 = 14. Then, 14 x 12 = 168. This approach is straightforward and easy to follow.
-
Method 2: Grouping for Efficiency: We can group numbers for easier calculation. For instance, recognizing that 2 x 12 = 24 simplifies the equation to 7 x 24. Multiplying 7 x 24 yields 168. This method highlights the commutative property of multiplication, emphasizing that changing the order of the numbers does not alter the final product.
-
Method 3: Distributive Property: The distributive property allows us to break down complex multiplications into simpler ones. While less efficient in this specific case, it's a valuable concept for more complicated equations. We could rewrite 12 as (10 + 2), then distribute the 7 x 2 across both: (7 x 2) x 10 + (7 x 2) x 2 = 140 + 28 = 168.
Beyond the Calculation: Exploring Related Mathematical Concepts
Solving 7 x 2 x 12 provides an opportunity to explore several key mathematical concepts:
-
The Commutative Property: The order of numbers in a multiplication equation doesn't affect the final product. 7 x 2 x 12 = 12 x 7 x 2 = 2 x 12 x 7, and so on. This property simplifies calculations and is crucial for understanding more advanced mathematical operations.
-
The Associative Property: The grouping of numbers in a multiplication equation doesn't affect the final product. (7 x 2) x 12 = 7 x (2 x 12). This allows for flexibility in problem-solving, enabling us to choose groupings that make the calculation easier.
-
Factors and Multiples: The numbers 7, 2, and 12 are factors of 168. Conversely, 168 is a multiple of 7, 2, and 12. Understanding factors and multiples is fundamental to working with fractions, ratios, and other advanced mathematical concepts.
-
Prime Factorization: Breaking down a number into its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves) is a useful technique in various mathematical contexts. The prime factorization of 168 is 2³ x 3 x 7. This process helps in simplifying fractions, finding greatest common divisors (GCD), and least common multiples (LCM).
Real-World Applications of Multiplication
Multiplication isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it's a vital tool used in countless everyday scenarios:
-
Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items, especially when buying several of the same item (e.g., 7 packs of 2 pencils each at $12 per pack).
-
Cooking and Baking: Scaling recipes up or down requires multiplying ingredient quantities. If a recipe calls for 2 cups of flour and you need to triple the recipe, you'll need 2 x 3 = 6 cups of flour.
-
Construction and Engineering: Calculating areas, volumes, and quantities of materials frequently involve multiplication. Determining the amount of tile needed for a floor or the volume of concrete for a foundation is dependent on multiplication.
-
Finance: Calculating interest, determining total earnings based on hourly wages and hours worked, and managing budgets all require multiplication skills.
-
Data Analysis: In various fields, from science to business, analyzing data often necessitates multiplying values to determine averages, proportions, or other relevant metrics.
Multiplication in Advanced Mathematics
The seemingly simple concept of multiplication forms the foundation for many more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Algebra: Solving algebraic equations often involves multiplication and its inverse, division.
-
Calculus: Derivatives and integrals, fundamental concepts in calculus, rely heavily on multiplication and its properties.
-
Linear Algebra: Matrix multiplication, a cornerstone of linear algebra, extends the concept of multiplication to multi-dimensional arrays of numbers.
-
Probability and Statistics: Calculating probabilities and statistical measures often involves multiplying probabilities or frequencies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the easiest way to multiply 7 x 2 x 12?
A: The easiest method depends on individual preference. Grouping 2 x 12 = 24 first, then multiplying by 7, is often considered efficient.
-
Q: Is there a trick to multiplying large numbers?
A: Various mental math tricks and techniques can simplify multiplication, including using distributive property, breaking down numbers into easier-to-manage components, or using lattice multiplication. Practice is key to mastering these techniques.
-
Q: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A: Consistent practice is vital. Start with basic multiplication tables, gradually increasing the complexity of problems. Using flashcards, online games, and interactive apps can make learning more engaging and effective.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Multiplication
The seemingly simple equation 7 x 2 x 12 serves as a gateway to understanding the profound importance and wide-ranging applications of multiplication. From basic arithmetic to advanced mathematical concepts and real-world problem-solving, multiplication is an essential skill that underpins numerous aspects of our lives. By mastering this fundamental operation and exploring its related concepts, we build a robust mathematical foundation that will serve us well throughout our academic pursuits and beyond. The ability to perform accurate and efficient multiplication isn’t merely a mathematical skill; it's a tool for empowerment, enabling us to confidently navigate a world increasingly reliant on numerical understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Basic Unit Of Length
Sep 13, 2025
-
2 X 5 2 3
Sep 13, 2025
-
Are Lipids Soluble In Water
Sep 13, 2025
-
Lim X 5 X 5
Sep 13, 2025
-
Is 324 A Square Number
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 2 X 1 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.