41 Degree F To C
thesills
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
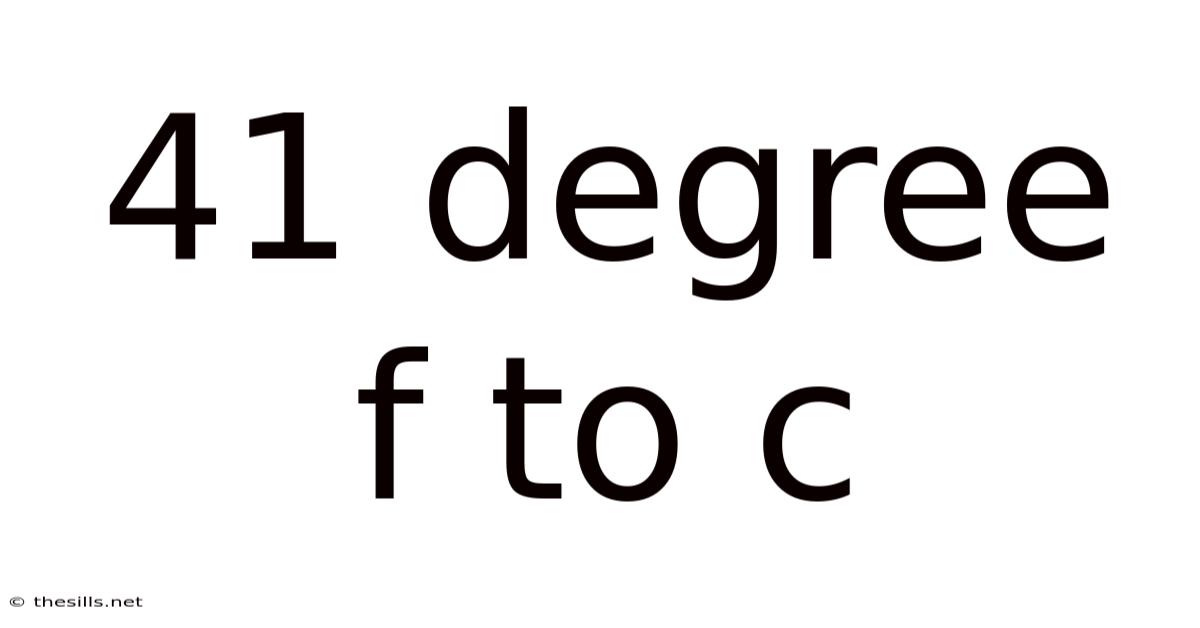
Table of Contents
Converting 41 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Many of us encounter temperature conversions in our daily lives, whether checking the weather forecast, baking a cake, or understanding scientific data. One common conversion involves switching between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C), the two most prevalent temperature scales. This article provides a detailed explanation of how to convert 41°F to Celsius, covering the mathematical formula, practical applications, and a deeper dive into the history and differences between the two scales. Understanding this conversion is crucial for various fields, from cooking and meteorology to engineering and medicine.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before we delve into the conversion, let's briefly examine the two scales. The Fahrenheit scale, invented by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, uses the freezing point of water as 32°F and the boiling point as 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C, again at standard atmospheric pressure. This simpler, 100-degree interval makes Celsius more intuitive for many scientific applications.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The fundamental formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula essentially takes the Fahrenheit temperature, subtracts 32 (to account for the difference in freezing points), and then multiplies the result by 5/9 (to adjust for the different scale intervals).
Converting 41°F to Celsius: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's apply the formula to convert 41°F to Celsius:
-
Start with the Fahrenheit temperature: 41°F
-
Subtract 32: 41°F - 32°F = 9°F
-
Multiply by 5/9: 9°F × (5/9) = 5°C
Therefore, 41°F is equal to 5°C.
Practical Applications of the Conversion
Understanding this conversion is vital in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Weather Forecasting: Many countries use Celsius for weather reporting. Knowing how to convert allows for easy comprehension of international weather information. A temperature of 41°F (5°C) indicates a cool, potentially chilly day, depending on other factors like wind and humidity.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Accurate conversion is crucial for achieving the desired results in cooking, particularly baking, where precise temperatures are essential.
-
Science and Engineering: In scientific research, engineering projects, and various industrial processes, accurate temperature readings and conversions are fundamental. Maintaining consistent temperatures is critical for experiments, machinery operation, and product quality.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature, medication storage, and various medical procedures require accurate temperature monitoring and often involve conversions between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
Beyond the Basic Conversion: Exploring Temperature Extremes
While the conversion of 41°F to 5°C is straightforward, understanding the broader range of temperatures and their implications is also beneficial.
-
Absolute Zero: Both Celsius and Fahrenheit are relative scales. They don't define the absolute absence of heat. This is represented by absolute zero, which is -273.15°C or -459.67°F. At absolute zero, all molecular motion ceases.
-
High Temperatures: Understanding the upper limits of temperature scales is also crucial. The melting point of iron is around 1538°C (2800°F), while the surface temperature of the sun is approximately 5,500°C (9,932°F). These values demonstrate the vast temperature ranges found in the universe.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Brief Overview
The development of temperature scales reflects the evolution of scientific understanding. Fahrenheit's scale, while widely used historically, is somewhat arbitrary in its reference points (using a brine solution and human body temperature). Celsius, with its more logical 100-degree interval between water's freezing and boiling points, offers a more straightforward and widely adopted scientific standard. The Kelvin scale, an absolute temperature scale, builds upon the Celsius scale by setting its zero point at absolute zero.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is the conversion formula (°F - 32) × 5/9?
A1: The formula accounts for the difference in freezing points (32°F vs 0°C) and the different scale intervals between the freezing and boiling points of water (180°F vs 100°C). The 5/9 factor adjusts for this difference in scale.
Q2: Can I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A2: Yes, the reverse conversion is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32.
Q3: Are there other temperature scales?
A3: Yes, besides Fahrenheit and Celsius, the Kelvin scale is a crucial scale in scientific applications. Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero.
Q4: What are the implications of a 5°C temperature?
A4: A temperature of 5°C (41°F) is considered cool. It's typically a chilly day, especially if there's wind or rain. Many people would wear a jacket or sweater in this temperature. Depending on location and individual sensitivity, 5°C can be considered pleasantly cool or uncomfortably cold.
Q5: What is the significance of using standard atmospheric pressure in defining freezing and boiling points?
A5: The boiling and freezing points of water are dependent on atmospheric pressure. At higher altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is lower, water boils at a lower temperature. Standard atmospheric pressure is a defined reference point (101.325 kPa) that ensures consistency and comparability of temperature measurements.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 41°F to 5°C is a relatively simple mathematical process. However, understanding the underlying principles of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, along with their practical applications, is crucial for various fields. The conversion formula provides a tool for seamless transitions between these two common temperature scales, improving communication and understanding across different contexts, from everyday life to advanced scientific research. Mastering this conversion demonstrates a foundational understanding of essential scientific concepts and their practical relevance. By understanding the historical context and the relative nature of temperature scales, one develops a more complete and nuanced understanding of this fundamental physical property.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Structure Of The Pollen Grain
Sep 12, 2025
-
Lewis Dot Diagram For Pcl5
Sep 12, 2025
-
Definition Of A Incomplete Flower
Sep 12, 2025
-
1 1 X 2 Derivative
Sep 12, 2025
-
Mediterranean Agriculture Intensive Or Extensive
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 41 Degree F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.